Why Predictive Maintenance?
Who likes unplanned downtime? Nobody.
Are you investigating the value that predictive maintenance could add to your organisation? Perhaps you have been dealing with machine breakdowns in the busiest of times and know that there are a lot of headaches involved when this happens. Unexpected downtime can seriously disrupt complex manufacturing supply chains. This bears high costs due to the limited productivity which can affect the whole supply chain.
This article series is a guide to assist you from getting the first idea to adopt PdM technologies to the actual implementation and maintaining such solutions.
We’ve heard about the Industrial Revolution 4.0, the rise of the Internet of Things, Big Data and the promise of predictive maintenance (PdM). But what is predictive maintenance?
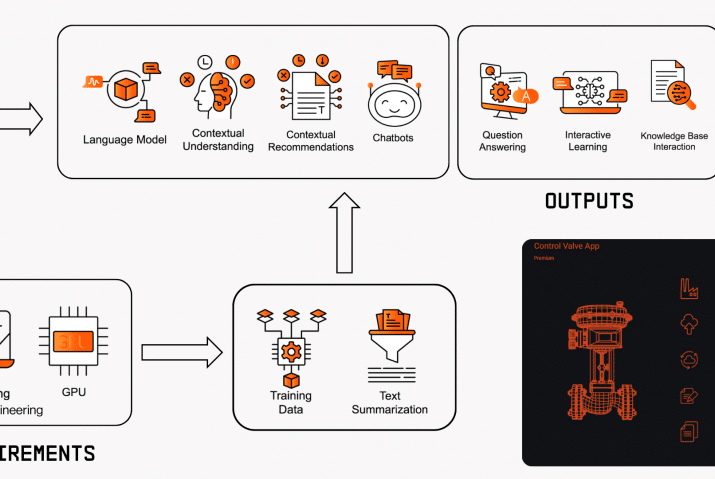
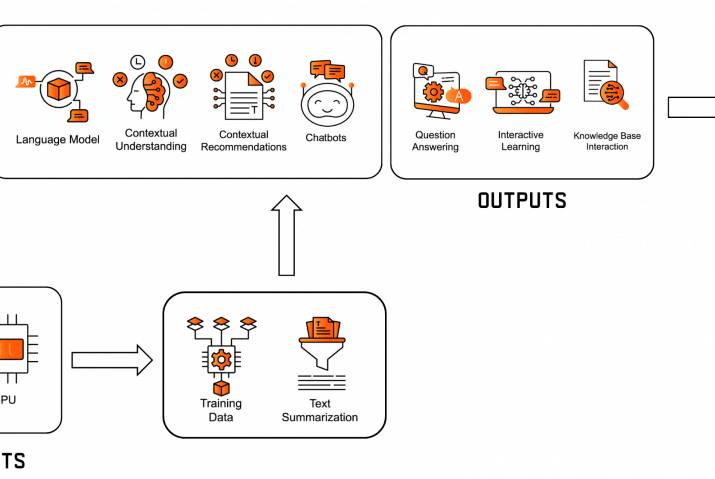
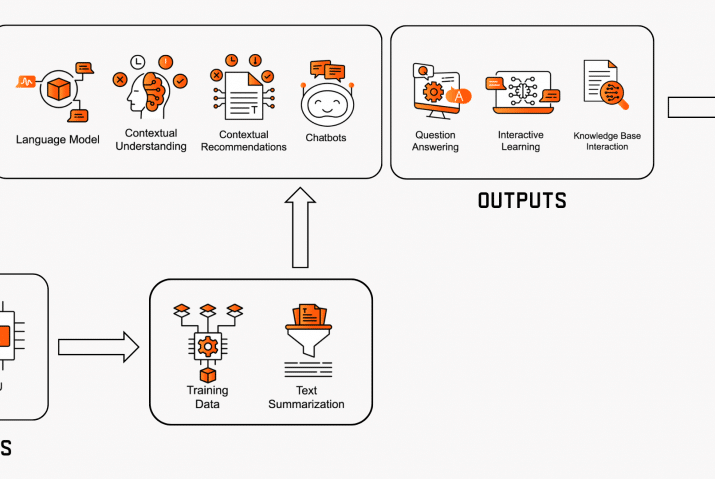
Predictive maintenance is a technique that relies on monitoring data and analyzing machine conditions to determine when equipment needs maintenance. Data collected by sensors, is used as the basis for advanced AI predictive algorithm development. These algorithms identify and estimate upcoming machine failures through real-time data processing. Insights from these PdM techniques provide improved support for maintenance decision-making. PdM delivers insights that notify the maintenance personnel about the current and the future state of the physical assets. For more detailed information about predictive maintenance have a look at our ebook.
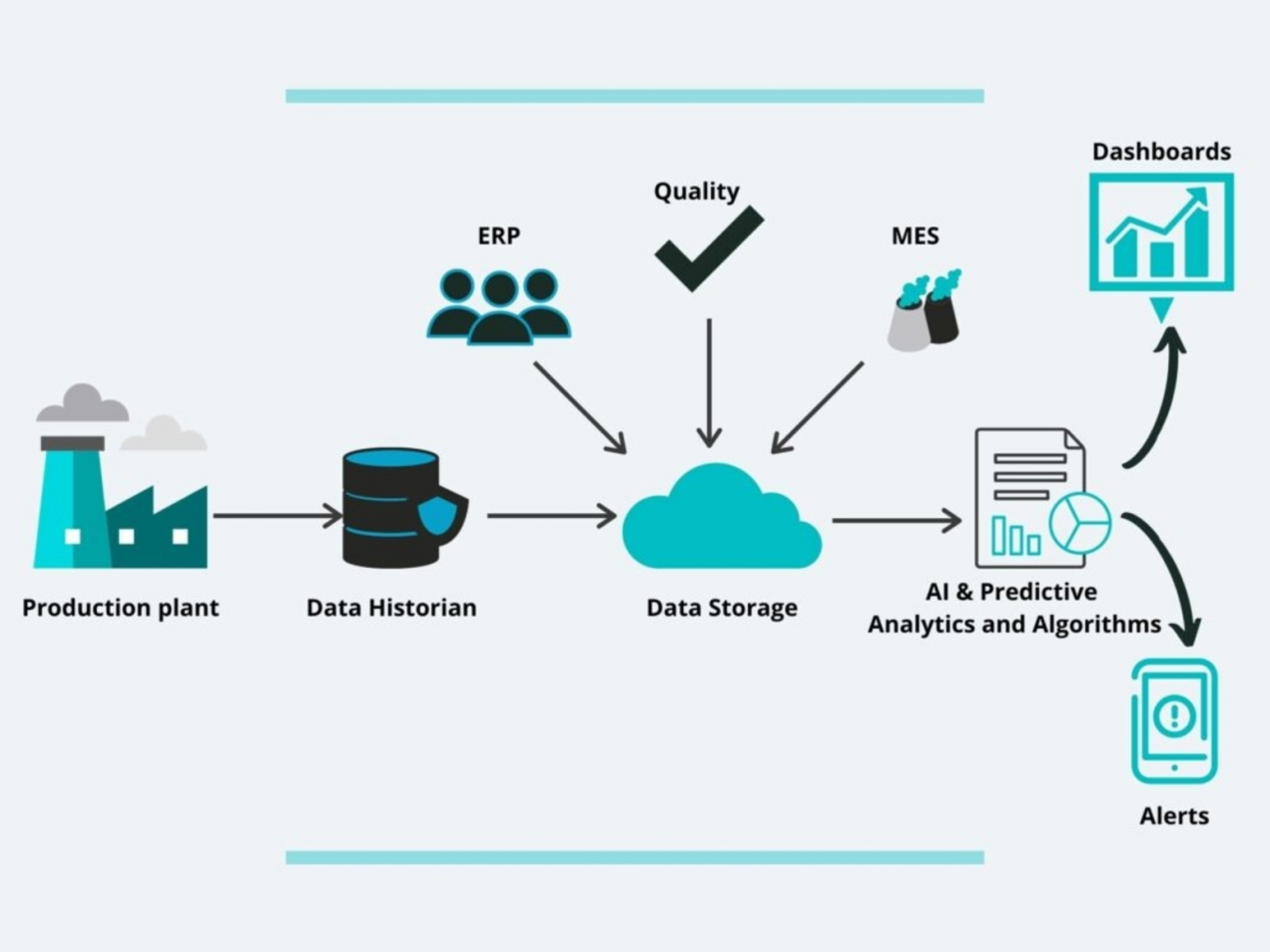
The Value of Predictive Maintenance
A report from the World Economic Forum and McKinsey indicates that the Fourth Industrial Revolution is expected to create up to $3.7 trillion in value by 2025. That is a considerable “pot of gold” to get your hands on by adopting these novel technologies associated with digitization, automation, advanced and predictive analytics, virtual and augmented reality and the industrial internet of things (IIoT). For example, Baoshan Iron & Steel company implemented predictive maintenance and achieved 30% of tool lifetime improvement, allowing them to maintain their competitiveness in the digital era.

Overview of PdM Project Phases
Implementing predictive maintenance is an organization-wide project. It is a multi-disciplinary process that requires full commitment from all levels of the company. Dividing PdM adoption into different phases helps you to better focus your efforts onto the right elements during each stage of the project.
Predictive maintenance projects can be divided into five phases: concept, feasibility, data, predictive algorithm development and operation phase:
Concept Phase – On the basis of a solid business case, the decision is made to pursue a PdM project. The scope and requirements of the project are defined and cost-benefit analysis is performed, resulting in a business case that gives an idea about return on investment of predictive maintenance implementation.
Feasibility Phase – The feasibility phase results in a running Proof of Concept (PoC) or Minimum Viable Product (MVP) that provides a limited demonstrator of the PdM solution. During the feasibility phase you will identify what barriers may be expected during actual full implementation of PdM. Barriers can be technical, people and organizational related, that prevent successful implementation of predictive maintenance technologies.
Data Phase – If the feasibility phase results in successful Proof of Concept, the next phase is initiated. The data phase targets the selection of fitting measurement techniques, the data acquisition and the preparation of data.
Predictive Algorithm Development Phase – When data is available in a suitable format, the development phase deals with the construction of algorithms for diagnostics and prognostics as well as training, tuning and validation of the algorithms that identify failures/functional degradations and time to failures/degradations.
Operation Phase – In the operation phase, real-time data access is provided and the solution is deployed. Regular revisions are made, and the solution is adjusted based on the new findings from data. Feedback from the system is taken into account, maintenance of the PdM platform is planned and further organization-wide roll-outs are carried out.
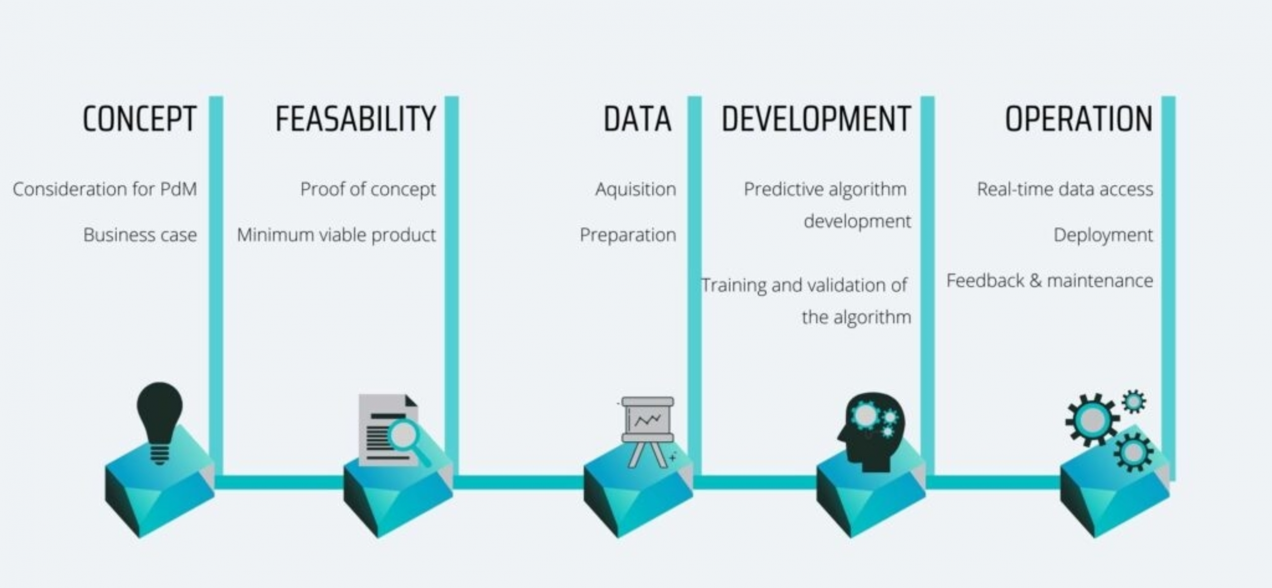
Each of these phases has a logical build-up towards the other. You cannot move forward with a project without having an understanding of what you want to achieve, having a clear vision. The idea is there, vision is clear, what now? It might be useful to investigate how feasible is the concept in the practical domain – you run a shortened project, Proof of Concept, in your organization to examine if the project would be applicable at full-scale. If the pilot is successful, then the data collection and preparation phase along with the following predictive algorithm development can be initiated. Finally, the operation phase is commenced with real-time data access and the solution is deployed.
Having distinct phases to predictive maintenance adoption allows you to have a more focused approach and successfully implement this technology. In the upcoming articles in this series we will dive deeper into each phase, detailing what to expect in each phase, what the enablers, best practices and barriers are. Continue to read this article series, you will learn what steps to follow in successfully running predictive maintenance projects.
APM Software E-book
Download our e-book to learn what UReason can do for you, find the unique functionalities of our next-gen APM software, look at the big data analytics framework and learn the different asset analysis models.