The International Data Spaces (IDS) is an initiative focused on creating a framework for secure data sharing and exchange in a decentralized manner across organizational and national boundaries. It aims to enable trusted data ecosystems where businesses can share data with confidence, maintaining control over their own data while benefiting from access to data from other sources. The IDS developments are managed by the International Data Spaces Association (IDSA), which is a not-for-profit association of more than 140 organisations, incorporated under German law. The IDSA creates standards for sharing data in data spaces, that allow participants to have full control over their data.
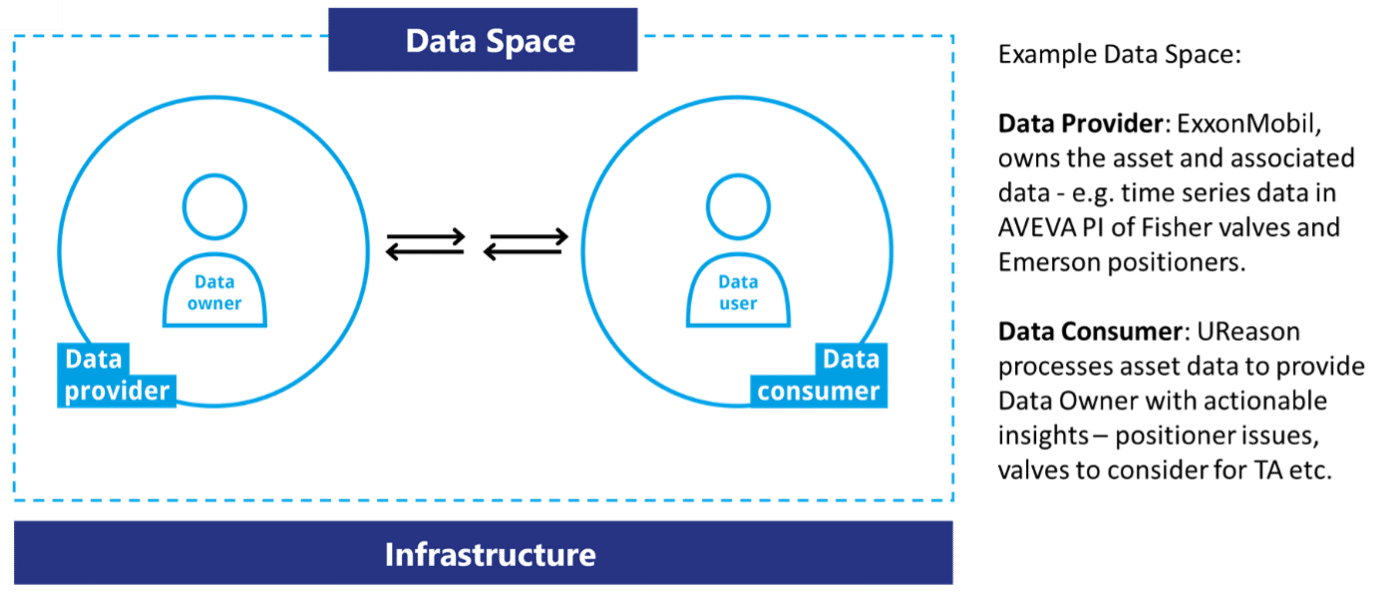
A Data Space is “a set of technical services that facilitate interoperable Dataset sharing between entities” (as defined in the IDSA Github). An example of a Data Space is illustrated below:
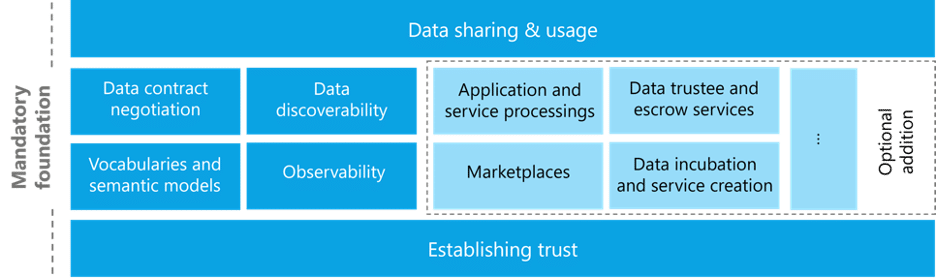
Based on compute infrastructure a Data Provider who owns assets and associated data, such as time-series data for control valves, shares this with a Data Consumer. The framework for sharing data needs to support several key features such as data security, privacy and usage control. Here the International Data Spaces plays an important role in providing a framework for:
- Data Sovereignty: The IDS framework emphasizes the importance of data sovereignty, ensuring that organizations retain control over their data and determine how it is shared and used.
- Interoperability: IDS promotes interoperability standards and protocols to facilitate seamless data exchange between different systems and platforms, regardless of technical or organizational differences.
- Security and Trustworthiness: Security and trust are paramount in the IDS framework. It employs advanced cryptographic techniques and security mechanisms to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of shared data.
- Data Usage Control: Organizations participating in the IDS ecosystem have granular control over how their data is used by others, including specifying access rights, usage policies, and conditions for data sharing.
- Privacy Protection: IDS incorporates privacy-preserving technologies and mechanisms to safeguard sensitive information and ensure compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation).
- Standardization and Certification: The initiative promotes the adoption of common standards and certifications to ensure consistency and trustworthiness across different implementations of the IDS framework.
- Facilitating Innovation and Collaboration: By enabling secure and trusted data sharing, IDS encourages innovation and collaboration among businesses, research institutions, and other stakeholders, driving digital transformation and the development of new products, services, and business models.
Overall, the International Data Spaces initiative aims to address the challenges associated with data sharing and exchange in a globalized and digitized economy, fostering a collaborative and trustworthy environment where organizations can leverage the full potential of their data assets while respecting privacy and sovereignty concerns.