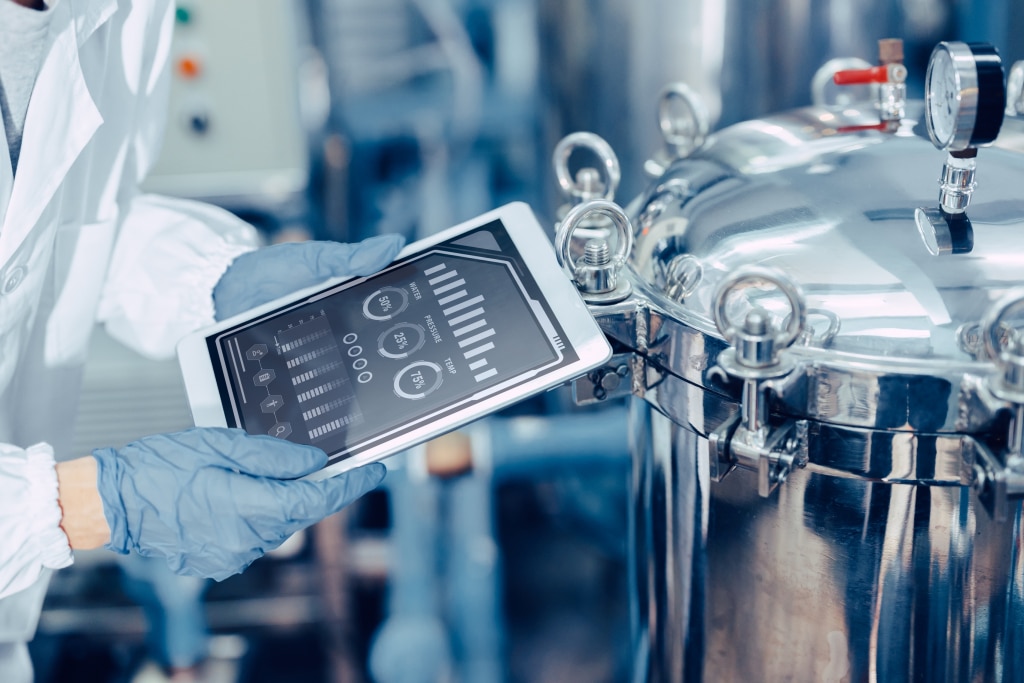
Energy efficiency is no longer a mere option for the process industry; it is a strategic imperative. According to the 2020 Annual Energy Outlook (AEO), the U.S. industrial sector’s total energy consumption is projected to increase by 36% from 2020 to 2050, the significance of improving energy efficiency cannot be overstated. The process industry, encompassing chemical, pharmaceutical, food and beverage, and many other sectors, stands at the forefront of this energy revolution. This article delves into the critical aspects of energy efficiency in the process industry, highlights successful case studies, and provides actionable tips for companies aiming to lead in this domain.
The Imperative for Energy Efficiency
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the chemical sector is the largest industrial energy consumer and the third-largest subsector in terms of direct CO₂ emissions. Around 50% of its energy input is consumed as feedstock (used as raw material rather than energy), with ammonia production being the highest emitter at 45%. Emissions must decline by about 15% by 2030 to align with the Net Zero Scenario. The pressing need for reducing carbon footprints and enhancing energy efficiency has never been more apparent.
Energy efficiency in the process industry is not just about cutting costs. It is about ensuring sustainability, improving competitiveness, and complying with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. The European Union, for example, has made energy efficiency a cornerstone of its energy policy, targeting a 32.5% improvement by 2030 compared to 2005 levels (European Commission).
Energy Efficiency as the “First Fuel”
Denmark has long advocated for energy efficiency as the “first fuel”—the most cost-effective and readily available resource to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The concept emphasizes that the energy saved through efficiency measures can be considered a primary energy source, akin to renewable energy. This approach has helped Denmark achieve a 29% improvement in industrial energy efficiency between 1990 and 2010 (State of Green), demonstrating that systematic focus and supportive policies can drive significant energy savings.
Energy Intensive Industries
Energy-intensive industries are critical to the global economy but are also among the highest consumers of energy, making them prime targets for efficiency improvements.
Here is a breakdown of energy-intensive industries according to EIA:
- Food – Food, beverage, and tobacco product manufacturing
- Pulp and paper – Paper manufacturing, printing and related support activities
- Basic chemicals – Inorganic chemicals, organic chemicals (e.g., ethylene propylene), resins, and agricultural chemicals; includes chemical feedstocks
- Refining – Petroleum refineries and coal products manufacturing, including coal and natural gas used as feedstocks
- Iron and steel – Iron and steel manufacturing, including coke ovens
- Nonferrous metals – Primarily aluminum and other nonferrous metals, such as copper, zinc, and tin
- Nonmetallic minerals – Primarily cement and other nonmetallic minerals, such as glass, lime, gypsum, and clay products
- Agriculture, forestry, fishing – Agriculture, forestry, and fishing
- Mining – Coal mining, oil and natural gas extraction, and mining of metallic and non-metallic minerals
- Construction – Construction of buildings (residential and commercial), heavy and civil engineering construction, industrial construction, and speciality trade contractors
Key Areas of Energy Consumption
In the process industry, significant energy consumption occurs in various areas, including:
- Pumping Systems: These account for 26% of total electricity consumption in the chemical sector (ABB).
- Compressed Air Systems: Essential for operations, yet often inefficient and energy-intensive. They typically consume 10% to 30% of the total electricity used in manufacturing facilities. This figure can be even higher in some industries, making it a significant target for energy efficiency improvements.
- Gas: Gas is used for the formation of base chemicals and for energy generation.
- Refrigeration and Heating Systems: Critical in food and pharmaceutical industries but can be optimized for better energy use.
Successful Case Studies
- BASF’s Energy Efficiency and Emission Reduction Initiatives: BASF, a global leader in chemical production, has implemented a comprehensive energy and emission management system across its production facilities. Since 1990, BASF has been able to lower its overall greenhouse gas emissions from operations by 57.8% and even reduce specific emissions (per metric ton of sales product) by 74.5% (BASF). The company’s Ludwigshafen site, one of the largest chemical complexes in the world, serves as a model of energy efficiency, incorporating advanced monitoring systems and sustainable practices to minimize energy use.
- Novo Nordisk and Ørsted Partnership: Danish pharmaceutical giant Novo Nordisk partnered with Ørsted (formerly Dong Energy) to reduce its CO2 emissions by 10% from 2004 to 2014. By implementing energy-saving projects and converting to renewable energy, the company achieved substantial savings and demonstrated that environmental responsibility can go hand-in-hand with business growth.
Trends and Technologies Leading the Way
- Variable Speed Drives (VSDs): VSDs are transforming energy management in process industries. By adjusting motor speed to match the load, VSDs can reduce energy consumption by up to 50%. This technology exemplifies how VSDs can enhance energy efficiency and safety (ABB).
- Synchronous Reluctance Motors (SynRM): SynRM motors offer up to 40% lower energy losses compared to traditional motors (ABB). These motors combine efficiency with safety, making them ideal for the process industry. Also, motors between 75kW and 200kW must meet the IE4 level as of July 2023 according to the European Union’s requirements (European Commission).
- Digitalization and Smart Monitoring: The integration of digital technologies enables real-time monitoring and optimization of energy use. Digital solutions provide insights into equipment performance, facilitating proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
EU Legislation: Strengthening Energy Efficiency Targets for a Sustainable Future
The European Union is at the forefront of global efforts to enhance energy efficiency, driven by its commitment to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and achieve climate neutrality by 2050. Recent legislative developments have further reinforced this commitment. The revised Energy Efficiency Directive, adopted in 2023, sets a binding target to reduce final energy consumption by 11.7% by 2030 (European Union), relative to the projected energy use for that year. This target is part of the broader “Fit for 55” package (European Council), which aims to cut greenhouse gas emissions by at least 55% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels.
In addition to these targets, the EU has introduced measures that require Member States to implement more stringent energy efficiency obligations. These include a mandatory 1.49% annual reduction in energy consumption for sectors like industry and transport from 2024 to 2030, and a 1.9% annual reduction in energy consumption in the public sector. The Directive also emphasizes the importance of renovations in buildings, which must meet the 3% annual renovation rate to ensure that the public sector leads by example in energy efficiency.
These legislative changes underscore the EU’s strategic approach to integrating energy efficiency across all sectors, with a focus on reducing reliance on fossil fuels, enhancing energy security, and driving sustainable economic growth
Tips for Enhancing Energy Efficiency
- Conduct Energy Audits: Regular energy audits identify inefficiencies and highlight areas for improvement. Companies should leverage advanced tools and software to assess and enhance their energy performance.
- Invest in High-Efficiency Equipment: Upgrading to high-efficiency motors, drives, and pumps can yield significant energy savings. The initial investment is often offset by reduced energy costs and lower maintenance expenses.
- Implement Energy Management Systems: Systems such as ISO 50001 provide a structured approach to managing energy use. These systems help companies set targets, monitor performance, and continuously improve their energy efficiency.
- Employee Engagement and Training: Cultivating a culture of energy awareness among employees is crucial. Training programs can empower staff to identify and implement energy-saving measures.
- Leverage Government Incentives: Many governments offer incentives for energy efficiency projects. Companies should explore subsidies, tax credits, and grants available in their regions to support their energy efficiency initiatives.
The Role of UReason and Asset Performance Management
UReason’s Asset Performance Management (APM) solutions are essential in enhancing energy efficiency within the process industry. UReason’s APM Studio helps companies optimize asset performance and energy use by integrating real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and smart maintenance strategies. This enables users to have detailed insights into energy consumption patterns, identify inefficiencies, and suggest actionable improvements.
The Road Ahead
As global demand for energy continues to rise, the process industry must lead by example in adopting energy-efficient practices. The shift towards sustainability not only addresses environmental concerns but also enhances operational resilience and market competitiveness. By embracing advanced technologies, conducting regular energy audits, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, companies can navigate the challenges of the future and thrive in an increasingly energy-conscious world.
In conclusion, energy efficiency is the bedrock of a sustainable and competitive process industry. Companies that invest in energy-efficient technologies and practices today will reap the benefits of reduced costs, enhanced sustainability, and a stronger competitive edge tomorrow. The journey towards energy efficiency is not just a business imperative; it is a commitment to a sustainable future for all.
For more information on how UReason can help your company achieve energy efficiency goals, explore our website and Asset Performance Management solutions. Together, we can build a sustainable future.
Learn More About APM Studio
Our product APM Studio is the leading Real-Time Analytics Software for Machines and Processes to make them Smarter.