Categories of Servitized Offerings
Servitized offerings broadly can be categorized into three distinct models, each reflecting a different customer mindset:
- Product-Oriented Offering: Customers purchase the equipment and may opt for additional services like installation or maintenance. They retain ownership and assume associated risks.
- Use-Oriented Offering: Customers pay for the usage of equipment (e.g., per hour or per mile) without owning it. The provider maintains ownership and includes services to ensure hassle-free usage.
- Result-Oriented Offering: Customers pay for a specific outcome or result (e.g., generation capacity of 100KW) without concern for the equipment used. The provider delivers the result, retaining ownership and associated risks.
Drivers of Servitization
Several factors motivate companies to adopt servitized business models:
- Meeting Evolving Customer Needs: Customers seek solutions that offer flexibility, reduced risk, and decreased maintenance responsibilities.
- Enhancing Company Performance: Service-based models can lead to increased revenue streams and stronger customer relationships.
- Competitive Differentiation: Offering unique service solutions helps companies stand out in saturated markets.
- Sustainability and Efficiency: Servitization can promote resource efficiency and support sustainability goals by optimizing product usage and extending lifecycles.
Challenges in Implementing Servitization
Transitioning to a servitized model presents several challenges:
- Organizational Transformation: Shifting from a product-centric to a service-centric approach requires significant changes in company culture, structure, and operations.
- Developing Service Capabilities: Companies must build or enhance capabilities to deliver and manage services effectively.
- Risk Management: Providers assume greater responsibility and risk, necessitating robust risk assessment and management strategies.
- Customer Relationship Management: Building and maintaining long-term relationships become crucial, requiring a deep understanding of customer needs and expectations.
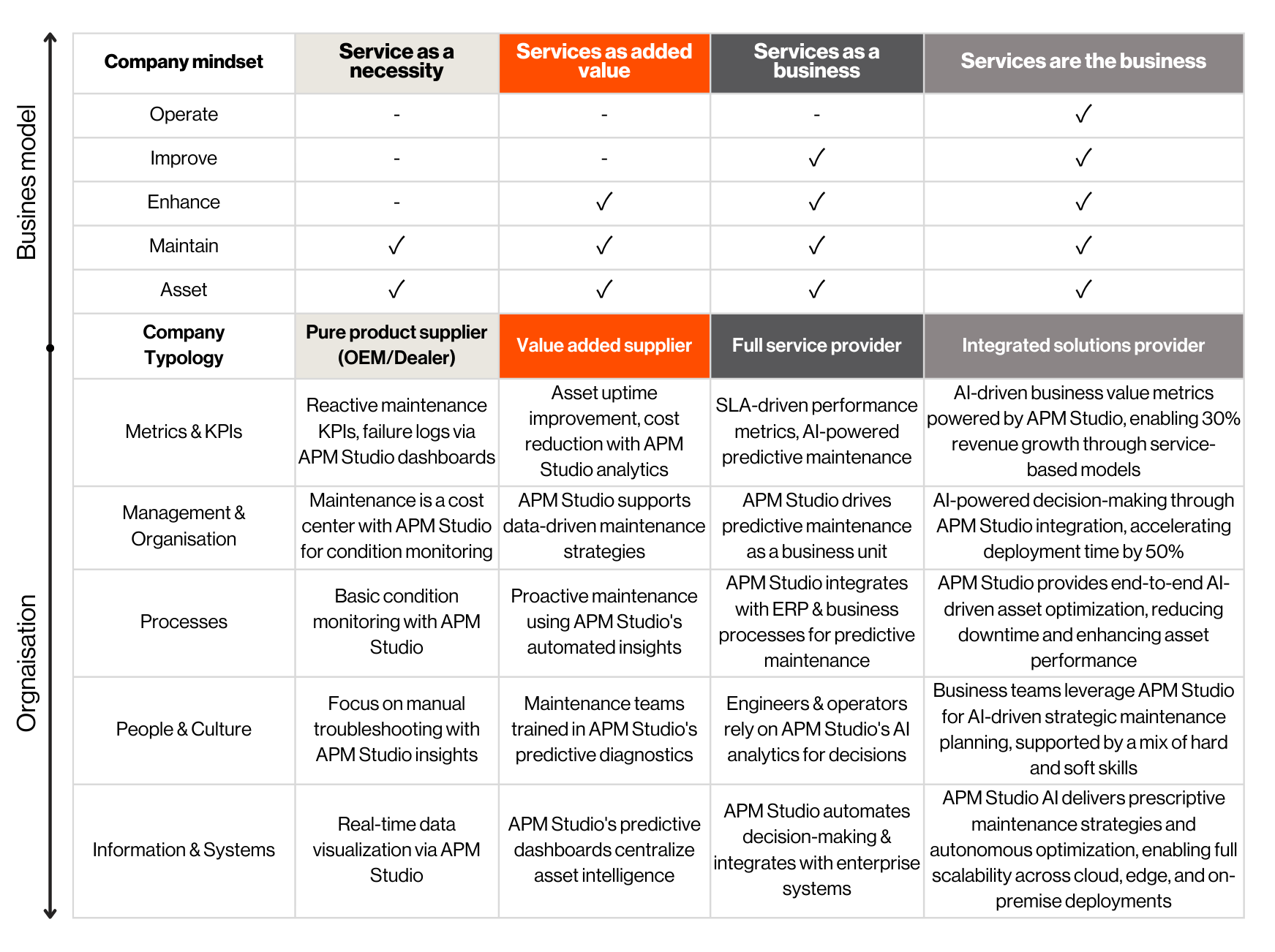
Servitization Maturity Model
The Praetimus Servitization Maturity Model, which outlines the stages companies typically progress through as they develop their service offerings:
- Exploration: Investigating the potential of adding services to products.
- Engagement: Developing initial service offerings and engaging with customers to refine them.
- Expansion: Broadening the range of services and integrating them more deeply into the business model.
- Excellence: Achieving a high level of proficiency in delivering services, with a strong focus on continuous improvement and innovation.
Key Considerations for Success
To successfully implement a servitized business model, companies should consider the following:
- Customer-Centric Approach: Develop a deep understanding of customer needs and design services that provide tangible value.
- Integrated Solutions: Combine products and services into seamless solutions that address specific customer requirements.
- Flexible Contracts: Create clear and comprehensive service contracts with customized terms to manage expectations and reduce the risk of disputes.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly assess and refine service offerings based on customer feedback and changing market conditions.
- Collaborative Partnerships: Work closely with customers and other stakeholders to co-create value and ensure the success of the servitized offering.
Conclusion
Servitization represents a significant shift in how companies create and deliver value. By transitioning to service-based business models, manufacturers and distributors can meet evolving customer needs, enhance performance, and achieve competitive differentiation. However, this journey requires careful planning, organizational transformation, and a steadfast commitment to understanding and serving customers.
Ready to Explore Our Demo?
If you’re considering a shift toward servitized business models, our interactive demo is the perfect place to start. Experience firsthand how integrating services with products can drive value, enhance customer relationships, and create sustainable revenue streams. Walk through key steps in servitization, from product-oriented to result-oriented offerings, and see how businesses can optimize asset usage, manage risks, and deliver outcomes more efficiently.
Click through the demo to discover how servitization can transform your business strategy!
Learn More About APM Studio
Our product APM Studio is the leading Real-Time Analytics Software for Machines and Processes to make them Smarter.