A control valve that is critical, from an operational perspective, typically maintains precise control over process variables such as flowrate, pressure, temperature and fluid level. Its proper functioning plays an essential role in your production process and contributes to quality, performance, safety and environmental compliance. Failure of critical control valves typically leads to significant consequences such as safety hazards, environmental damage, production losses, or equipment damage.
But control valves can also be critical from a maintenance perspective. On-site repairs may not be possible, it may need to be remanufactured causing severe production outage or it may not be flanged but welded in place causing planning and permit headaches.
Avoiding critical control valve failure involves a combination of proactive maintenance strategies, proper installation and operation, and most importantly continuous monitoring. Some of the key activities to prevent critical control valve failures are:
- Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Implement a comprehensive inspection and maintenance program for critical control valves. This must include routine inspections to identify signs of wear, corrosion, leakage, or other issues. Scheduled maintenance tasks such as lubrication, cleaning, and calibration should also be performed according to manufacturer recommendations or industry best practices. Note that you can safe considerable time on inspection by adopting a continuous monitoring program (mentioned below).
- Correct Installation: Somewhat of an open-door, but still ensure that critical control valves are installed correctly according to manufacturer specifications and industry standards. Proper installation includes appropriate alignment, sufficient support, correct valve sizing, and proper sealing to prevent leaks or premature wear.
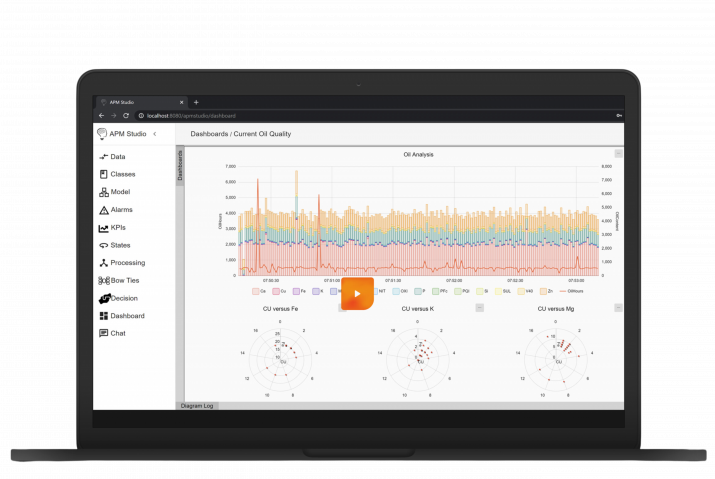
- Monitoring and Condition Monitoring: Implement a monitoring system to track the performance of critical control valves continuously. This does NOT have to involve placing new sensors or instrumentation to detect early signs of degradation or impending failure. The data you very likely store in your data historian, related to your critical control valves, will be the SP/PV and likely the CO and MV. Using this data the Control Valve App can identify abnormalities, deviations from normal operating conditions and provide early notifications to operations and maintenance personnel.
- Proactive Replacement or Repair: Replace or repair critical control valves before they reach the end of their service life or exhibit signs of imminent failure. Develop criteria for determining when a valve should be replaced based on factors such as wear, performance degradation, or changes in process conditions. Consider implementing a predictive maintenance program that utilizes condition monitoring data to schedule maintenance or replacement activities proactively. Here the Control Valve App also strongly supports you in your TA activities with Remaining Useful Lifetime indications and planning deadlines – Also see the Valve World Article.
- Emergency Preparedness: Develop contingency plans and emergency procedures to respond quickly to control valve failures or malfunctions. Ensure that personnel are trained on emergency shutdown procedures and that backup systems or redundant valves are in place to mitigate the impact of a valve failure.
- Documentation and Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of critical control valve maintenance, inspection, and repair activities. Keep track of valve performance data, maintenance history, and any modifications or upgrades made to the valves. Again, here the Control Valve App actively supports you in performance monitoring!
Following these key activities and implementing a proactive approach to maintenance and monitoring, organizations can minimize the risk of critical control valve failures and ensure the reliable operation of their processes.
But there is more: to quantify the business benefits of continuous valve diagnostics we have worked closely together with our customers to define a business case calculator. The business case calculator allows you to quantify and objectively calculate the maintenance/inspection savings, turn-around and down-time savings.
For specific markets, such as energy distribution networks, energy savings are also calculated. Next to these there are the more difficult quantifiable savings of continuous valve diagnostics. We can’t put an ROI on safety, knowledge capture and supporting digitization initiatives. Wondering why product losses are not quantified? Well, they are but not easily shared.
Want to get started with the business case calculator? Just fill in the form and we’ll contact you!